
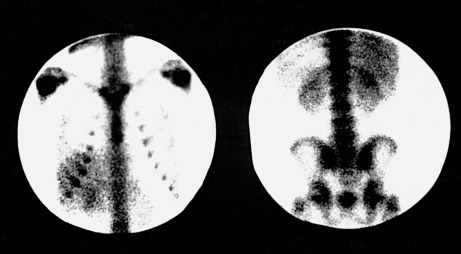
The carbon-14 in an organism is continuously being replenished till the organism is alive and its quantity starts to reduce by emission of beta rays.
The interaction of cosmic ray and nitrogen atoms results the formation of carbon-14 naturally in the atmosphere.Ĭarbon dioxide formed from carbon-14 is absorbed by plants and passed on to the food chain. The time of death of an organism can be estimated easily by determining the quantity of carbon-14 available in a dead organism. By far the most common use of carbon-14 is in archaeological dating. Carbon-14Ĭarbon-14 is the radioactive isotope of carbon having 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Reacting with oxygen it converts into water form and being a part of the food chain. It is also available in nature in very small amount. Tritium is also formed in nuclear reactors carrying out fission reaction as by products or through various nuclear weapon explosions. Tritium is naturally occurring isotope, which means it forms naturally by means of cosmic rays which fall on the nitrogen molecule breaking it to form tritium. It has 2 neutrons in its nucleus and one proton. The lightest radioactive isotope is of hydrogen, which has a mass number of 3 and called Tritium. Radioactive Isotopes Examples Detailed ExplanationsĮxamples of radioactive isotopes and their usage can found in almost all fields of modern science, whether it is medicine, biology, food preservation, mining, industrial applications, astronomy, particle physics etc. They can occur both naturally as well as synthesized artificially. A few of the radionuclei have very high half-lives ranging above 100 million years such as Uranium and thorium. The decay times of a radionuclei vary widely and it is designated by its half-life.Īround 2400 radionuclei have half-lives less than 60 minutes, most of which are produced artificially. The unstable radioactive isotopes decay emitting alpha, beta or gamma rays to form the stable nuclei or sometimes another unstable nuclei or radionuclei as it is commonly called. Plutonium-239 has a half-life of 24,000 years. Strontium-90 and cesium-137 have half-lives of about 30 years (half the radioactivity will decay in 30 years). Radioactive isotopes are unstable isotopes of chemical elements which have different atomic mass than defined by the periodic table. Radioactive Isotopes Examples are listed below:

Some isotopes decay in hours or even minutes, but others decay very slowly. Radioactive isotopes eventually decay, or disintegrate, to harmless materials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
